NEC Corporation has recently conducted successful IoT (Internet of Things) trials at Japan’s Haneda Airport, which included monitoring the positions of cargo transport vehicles and tracking the movements of mechanics at an aircraft maintenance hangar.
The trials where performed between July and August this year on behalf of Japan Airlines, which seeks to improve the efficiency of its operations at the airport. The IoT trials were done both inside and outside the airport in order to identify specific conditions, such as restrictions on the installation of devices and operating IoT in a vast outdoor business area.
 “We are very satisfied with the results of the project using NEC's consulting services, which helped us examine technological feasibility and identify issues. We expect further technological collaboration with NEC and their advanced IoT solutions,” said Kazuhiro Kurita, vice president and deputy general manager, IT Planning and Management Department, JAL.
“We are very satisfied with the results of the project using NEC's consulting services, which helped us examine technological feasibility and identify issues. We expect further technological collaboration with NEC and their advanced IoT solutions,” said Kazuhiro Kurita, vice president and deputy general manager, IT Planning and Management Department, JAL.
In these trials, NEC verified the effectiveness of IoT using LoRaWAN and Bluetooth from a wide variety of communication methods (multi-connectivity) and provided consulting based on its knowledge and technologies related to networks.
NEC's “Trial Pack for Starters”, which provides a total package of IoT devices, servers, and applications for users to test the collection and visualisation of data, enabled these trials to be quickly started following just three weeks of preparation.
Tracking the position of cargo transport vehicles
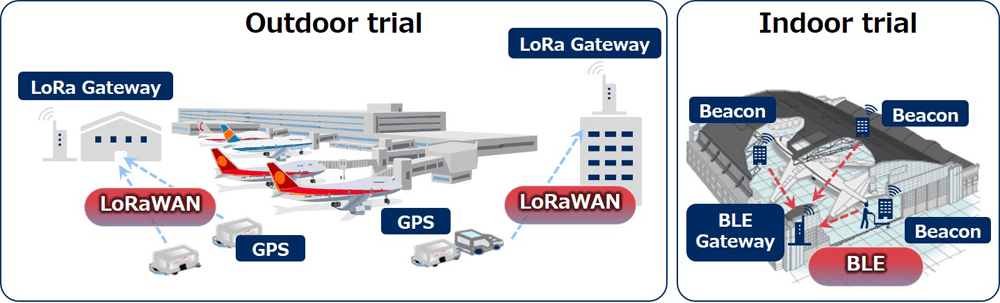
Cargo transport vehicles travel extensively throughout the vast grounds of an airport, and in order to operate efficiently, it is important to place them in the right place at the right time.
During the trials, NEC installed GPS devices on the vehicles and built LoRaWAN networks using LoRa gateways. Two sets of LoRa gateways were enough to cover almost all of the outdoor space at Haneda Airport, enabling JAL to determine the position of cargo transport vehicles in real time.
This confirmed the effectiveness of LoRaWAN for communicating in a wide area while minimising the introduction of equipment.
Understanding mechanics' movements
In order to pass on know-how from experienced mechanics to additional workers and improve work efficiency, it is useful to understand the movements of mechanics in their work areas.
During the trials, personnel from JAL and NEC were equipped with BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) devices as they simulated the work of mechanics in tool rooms, a maintenance hangar and offices that were connected to BLE networks.

As a result, it was possible to accurately detect the positions of individuals and track trends in different environments – such aircraft, work scaffolding, and walls – where radio waves are easily reflected or interfered with.
“These demonstration trials with JAL are part of the NEC Smart Connectivity initiative, where we have capitalised on network flexibly to connect data generated by people and goods beyond the industrial framework,” said Naohisa Matsuda, deputy general manager for Digital Services Solution Division, NEC Corporation.
He added: “Going forward, we aim to continue to contribute to the improvement of JAL's customer services and the efficiency of airport operations.”



