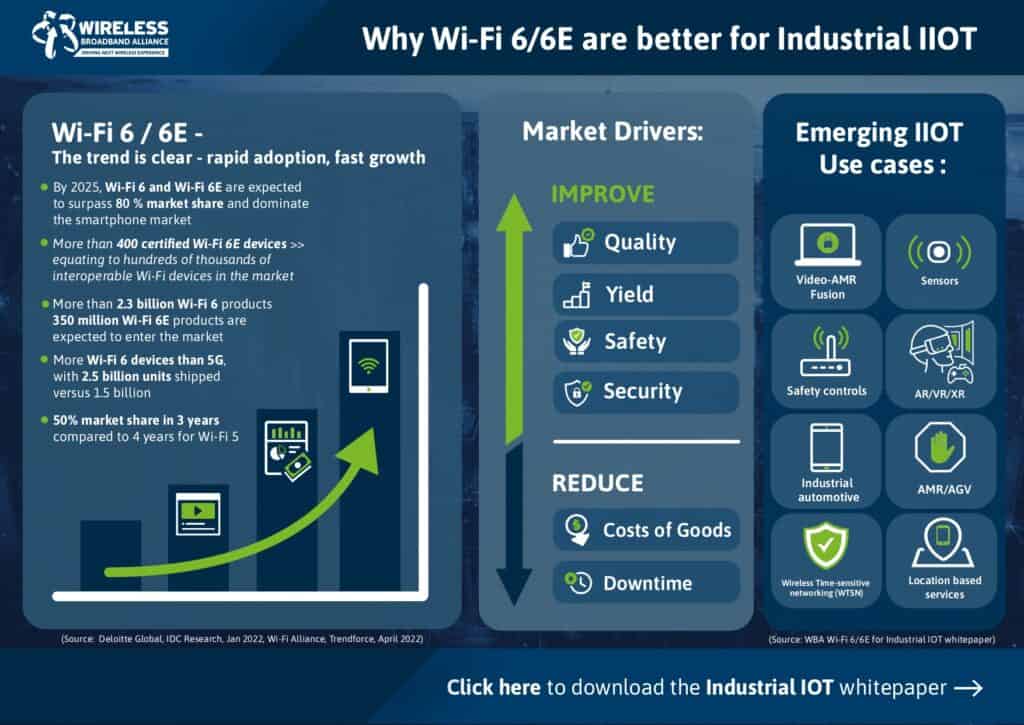
The Wireless Broadband Alliance (WBA) yesterday released a report that explores how Wi-Fi’s latest features are ideal for meeting the unique, demanding requirements for a wide variety of existing and emerging IIoT applications.
“Wi-Fi has been a key enabler of the global IIOT market, which is on track to have a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of about 23% between 2017 and 2023. Wi-Fi 6 and 6E are expanding capabilties by providing the multi-Gb/s data rates, additional spectrum, deterministic performance and other advanced capabilities necessary to support demanding applications such as Industry 4.0,” said Tiago Rodrigues, CEO of the Wireless Broadband Alliance.
Entitled “Wi-Fi 6/6E for Industrial IoT: Enabling Wi-Fi Determinism in an IoT World”, the white paper delves into the efficacy of using the latest Wi-Fi standard for new IIoT applications deployed manufacturing/Industry 4.0 and logistics, involving autonomous mobile robots (AMRs), automated ground vehicles (AGVs), predictive maintenance and augmented/virtual/mixed reality (AR/VR/MR).
“As more equipment is monitored, wiring becomes prohibitive,” the paper says. “Industry is moving towards the inclusion of wireless technologies to lessen the cost of obtaining more information about their processes. In one recent case in the oil and gas industry, moving to a wireless installation resulted in a 75% cost reduction in installation.”
For example, manufacturers are increasingly using IIoT sensors for vibration, temperature and lubricant viscosity to catch emerging equipment problems before they result in extensive, expensive downtime. Other IIoT sensors provide real-time insights about production output, inventory levels and asset locations. Wireless has become the preferred way to network these sensors because it’s faster and cheaper to deploy than copper or fibre.
Industry-wide initiative towards next-generation Wi-FI
According to Eric McLaughlin, vice president of the Client Computing Group and general manager of the Wireless Solutions Group at Intel Corporation, said that Wi-Fi is an essential ingredient in enabling the major transformation now happening in the industrial IoT market.
“Applications like Autonomous Mobile Robot (AMR) and Remote Human Management Interface (HMI) industrial devices require the mobility, functional safety, high reliability, low latency, robust security and determinism that Wi-Fi 6/6E can deliver particularly when combined with TSN (time sensitive networking) solutions. We are pleased to be leading this Wi-Fi technology evolution, and applauds the work that the WBA is doing in this space.”
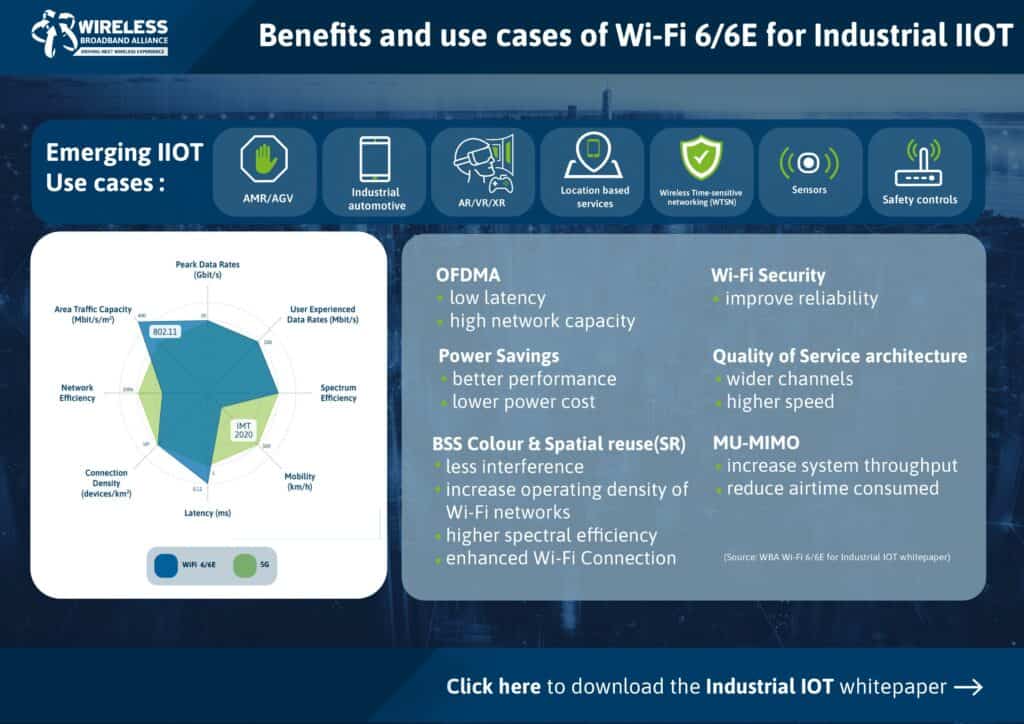
Produced by WBA’s Wi-Fi 6/6E for IIOT work group led by Intel, Cisco and Deutsche Telekom, the report provides an overview of Wi-Fi 6 and 6E capabilities that are ideal for sensors and other IIoT applications, such as:
- Scheduled access (SA) enabled by trigger-based (TB) uplink (UL) orthogonal frequency domain multiple access (OFDMA) in Wi-Fi 6 provides the ability to reduce or eliminate contention and bound latency (e.g. 99 percentile). This leads to increased levels of determinism applicable to all real-time and IIOT applications.
- Wi-Fi 6 provides many deterministic QoS capabilities, such as the traffic prioritization that is a key component of Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) for Industry 4.0 applications. Another example is Multi-link operation (MLO), a capability that helps provide high reliability for applications that cannot tolerate any packet loss.
- The Fine Timing Measurement (FTM) protocol specified in IEEE 802.11-2016 enables both time-synchronization but also precise indoor range and position/location determination. This can be used for Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMR) and Automatic Guided Vehicles (AGV) applications such as route planning, exception handling and safety-related aspects including collision avoidance based on proximity. This capability does not require additional Wi-Fi infrastructure, so manufacturers can implement it immediately, for instance as part of their Industry 4.0 migration.
- The target-wake-time (TWT) feature added to Wi-Fi 6 provides more efficient power-save and scheduling enhancement. This capability is a good fit for battery-powered IIoT nodes that need to transmit only infrequently, such as a sensor that uploads data only when a motor’s temperature exceeds a certain threshold.
- Wi-Fi 6E supports up to 1.2 GHz of spectrum, making it ideal for use cases that require both multi-Gb/s throughput and determinism, such as industrial AR/VR/MR and sensor fusion.
The 52-page report also includes RF/network deployment guidelines for factory, warehouse, logistics and other use cases. For example, it provides recommendations for leveraging 802.11ax/Wi-Fi 6 scheduling capabilities to optimize traffic patterns and manage critical QoS requirements. Another example is using high-gain directional antennas to increase channel re-use rates and work around metal racks and other signal-attenuating features commonly found in warehouses.
Ongoing projects around next-gen Wi-Fi
The WBA said there are over three dozen vendors, service providers and other organisations participated in developing the white paper.
Some current projects around the new Wi-Fi standards that have been mentioned in the paper include:
- Cisco, Intel and partners are working on use cases involving AMR and AGV, where key requirements include <10-20ms latency, <50km/h speed and .99.9999% reliability.
- Cisco and Mettis Aerospace are working on sensor applications, where requirements include very high reliability, low power consumption and high device density.
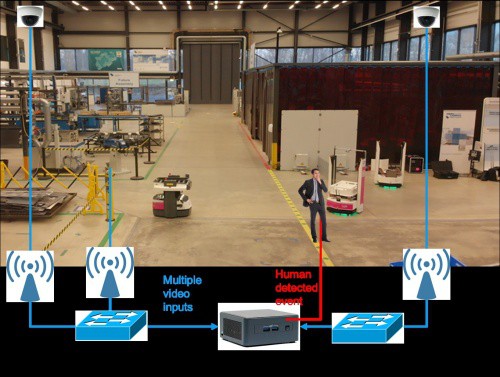
- Further work taking place on video-AMR fusion use cases such as collision avoidance, where technical requirements include <20ms latency and <1ms jitter.
- Cisco is working on safety control applications, which require <1-ms latency for applications such as automatically stopping a machine after a sensor detects that the person has left the operating position.
- Cisco, Mettis Aerospace and Intel are working on AR/VR applications with resolutions up to 80K and 90fps, where throughput requirements can be as high as 100 Mb/s.
- Cisco is working on automotive uses cases such as logistics in high-density storage lots, where <60dBm interference is key for reliable operation.
Matt MacPherson, CTO, Cisco Wireless, said: “The next industrial evolution will not only depend on the ability to connect more things, but to also add greater reliability, intelligence and security. This can only be done when the world’s leading companies work together with progressive Industry 4.0 customers to explore and implement new, game-changing technologies.”
He added: “We are proud of the work we have done with the WBA to ensure customers understand how, when and where to apply the latest innovations. It is because of advancements in wireless technology that Industrial IoT sits at the centre of the forthcoming industrial revolution."
Ahmed Hafez, vice president of network convergence at Deutsche Telekom said: “Deutsche Telekom’s industrial partners are demanding ubiquitous high performance wireless connectivity to take their production processes to the next level. Converged Access combining 5G cellular and Wi-Fi6/6E Networks will play a vital role to deliver comprehensively on their application and process demands in the near future”.



