CollaboGate Japan (CG) has formed a business alliance with Tessera Technology (TSSR) to develop a decentralised IoT platform – a first in the world – that will use robust hardware-based security functionality of the Renesas' microcontrollers (MCUs) to verify contactless transactions conducted through IoT devices.
Tokyo-based CG provides Japan's first decentralized ID platform called UNiD, while the Yokohama-based TSSR, has strong expertise in IoT device software development.
The rise of the Stay-at-Home economy has accelerated the adoption of contactless transactions at the consumer level, and both companies see a huge business potential in providing verification of IoT devices used contactless transactions. Particularly with the shift to contactless transactions in smart bank branches, virtual concierges at healthcare and government services, digital orders at restaurants, and automated receptions at offices and hotels.
According to a Deloitte study, the market size of the contactless economy in Asia Pacific will reach US$11 trillion, double the current level.
“With the COVID-19 pandemic, the number and type of businesses that need to interact with users contactless have exploded beyond the specific industries. We believe that the verifiable data exchange platform between "people" and "machines" in a decentralised manner, will support the transformation to contactless systems in a wide range of fields, including new work styles, mobility, logistics, and smart cities, and will contribute to progress our digital society. We are pleased to be the first mover in the world to take on this challenge,” said Masayoshi Mitsui, CEO, CollaboGate Japan.
A decentralised IoT platform
With the alliance, both companies will be working on a proof-of-concept project that intends to build a "decentralised IoT platform" that smoothly connects people and things, and a "smart concierge" that enables the contactless economy by using "UNiD" decentralized ID platform developed by CG and TSSR's expertise in embedded system development on Renesas’ MCUs.
“In the current Internet system, it is difficult to automatically verify the data provided by users without a trusted third party. In reality, the manual verification process of the data is still necessary for businesses. By introducing a decentralised identity mechanism to IoT devices, we can build a mechanism that allows them to autonomously verify the data provided by users. This will enable the safe and quick delivery of services of their needs,” the companies said in a press statement.
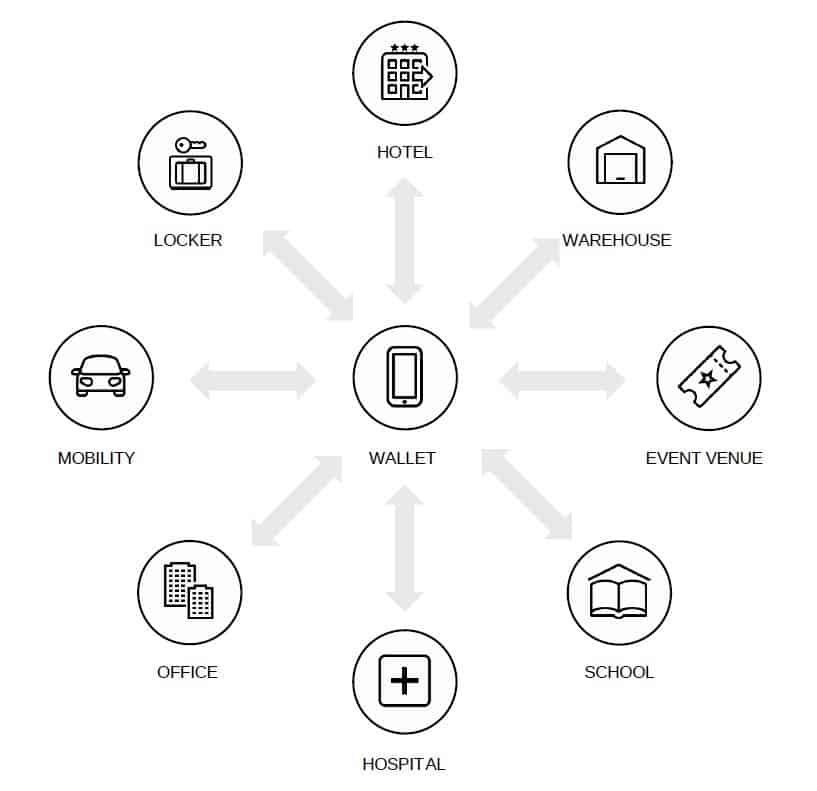
They added: “In this project, we will build a prototype of a "smart concierge" with an identity verification function for use in BFSI, healthcare, government, and access management at offices, hotels, factories, logistics warehouses.”
IoT devices must be able to correctly identify, authenticate, and authorised users, automatically verify the data applied for, consider user privacy, and ensure the security of unattended IoT devices. A decentralised IoT platform that meets these requirements is needed for a smooth transition from the face-to-face to the non-face-to-face system.
CG”s and TSSR’s “smart concierge model has four steps: first, service provider issues credentials (identity verification information, usage permit) to the user's mobile wallet; second,the user sends the credentials stored in the wallet to the IoT device; third, the IoT device verifies the credentials and opens/closes the gate; and fourth, access log is sent to the cloud server.
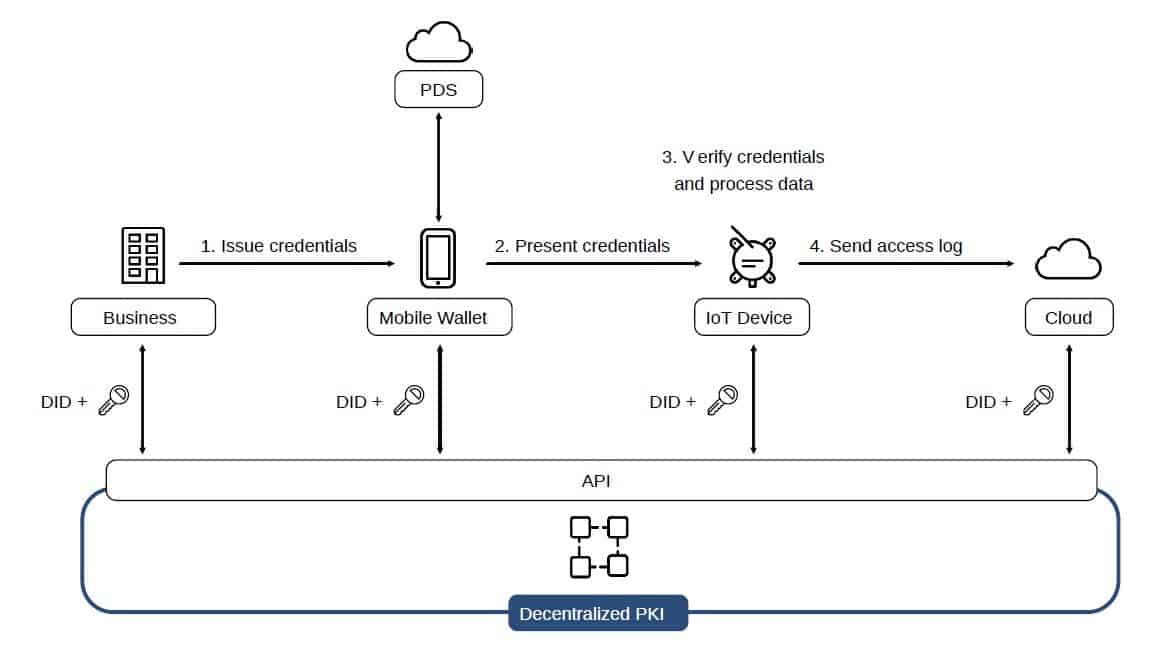
With the smart concierge model, people can check in to hotels, accommodations, and other lodging facilities and unlock their rooms by simply carrying their mobile app. It can also streamline the validation and entrance for live music, concerts, baseball, football, and other sports, as well as theme park facilities. The system is also expected to enable contactless operations and efficiency that have been conducted face-to-face, such as the efficient management of office visitors, logistics warehouses, medical and educational facilities.
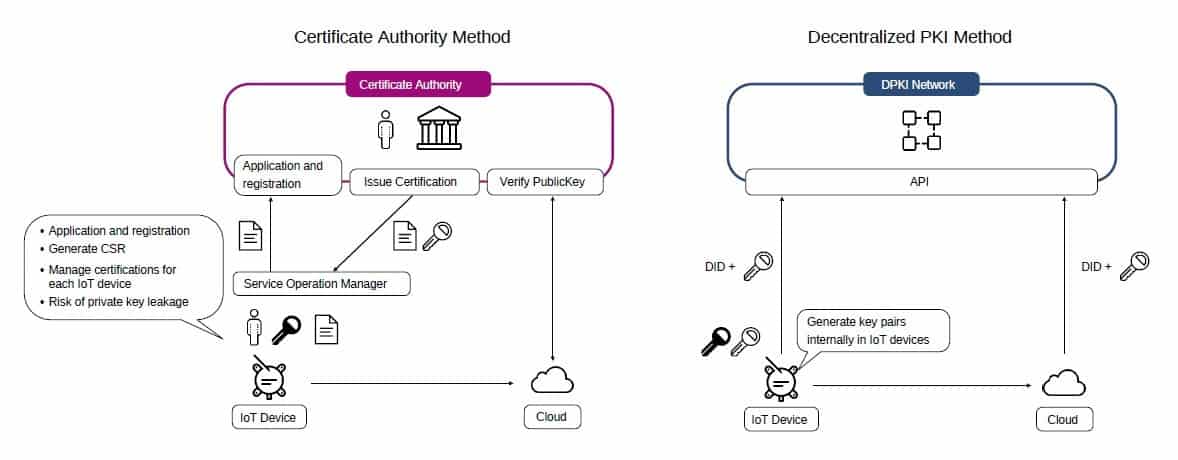
Raising IoT security
IoT devices that are connected to the network are subject to security risks such as hacking and identity theft. For one, the access IDs and passwords hard-coded into IoT devices are vulnerable if they are left as default settings or are easy to guess. In fact, there was a case where a large number of IoT devices were illegally accessed and used as a botnet to launch DDoS attacks.
For this reason, security by the PKI standards has significant advantages over the password method. However, the conventional PKI standards using CA certification authorities require manual management of many certificates for each IoT device. In addition to being a very time-consuming task, there are risks such as the leakage of private keys managed by the service operator. In addition, the time and effort required to renew certificates lead to the use of certificates with a long expiration date, which causes vulnerabilities. Thus, the conventional PKI standards have problems in terms of cost, operation, and security.
By introducing a decentralised ID mechanism to IoT devices, first, a key pair is generated within the IoT device, then the public key corresponding to the digital signature is registered in the decentralised PKI network. Anyone from the network can reference this public key, and a cloud server communicating with the IoT device can retrieve this public key and verify the digitally signed data. This is expected to eliminate the need for manual verification, increase security strength, and significantly reduce the operating costs of IoT devices.
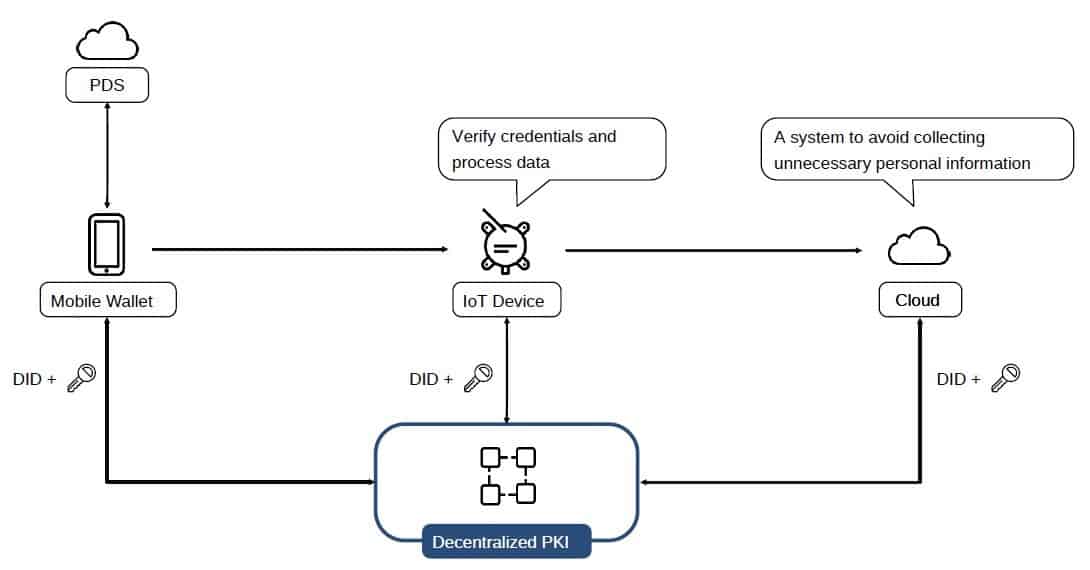
Enabling privacy-preserving data transactions
CG and TSSR will also design the decentralised IoT platform to comply with current regulations such as GDPR and CCPA, which impose a separation between holding data and using the data.
In Japan, the Act on the Protection of Personal Information is scheduled to take effect in April 2022, and the handling of personal data via IoT devices will require system design based on the same consideration of individual privacy. Decentralized IoT platforms provide a mechanism that enables IoT service providers to provide the desired services without retaining unnecessary personal information. It provides a mechanism for safe and smooth authentication and data transactions between people and IoT devices based on personal consent, using a mechanism where individuals control their personal information.
Sakae Ito, vice president of IoT Platform Business Division at Renesas Electronics is pleased to contribute in the decentralised IoT platform with its secure MCU/MPR technologies.
“We hope that this demonstration experiment of the decentralized IoT Platform by the CollaboGate and Tessera will prove IoT devices can bring security and reliability as well as improved convenience to users, expanding the demand for contactless applications,” he said.



