As the race towards high-end autonomous vehicles ramps up, automakers and their suppliers are exploring new software, tools, and architectures for developing self-driving platforms that rely on machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI).
The VDC Research, Automotive Software and Development Solutions, indicates that the move towards self-driving technology is blurring the lines between traditional organizations and their previously-entrenched roles in the automotive supply chain.
“Traditional software and tool vendors are responding to increasing demands for autonomous driving capabilities, functional safety, network security, and hardware consolidation that are manifesting across vehicles of all price points,” said Roy Murdock, IoT & Embedded Technology Analyst at VDC Research. “This increasing complexity is driving a reorganization of both where and how automotive software is designed and integrated.”
Level 3 self-driving systems are shaking up the market as the pursuit of hands-free autonomous vehicles is fuelling the recent explosion of interest, funding, and high-profile acquisitions in the automotive market. According to VDC, the timing is finally right for IoT connectivity, powerful processing hardware, ubiquitous camera, and sensor technology, and machine learning testing in the cloud to come together and bridge the gap between hands-on “assistance” to hands-off “automation”.
Figure 1: Global Revenue of Automotive Software & Development Tools, by Type (Percent of Market)
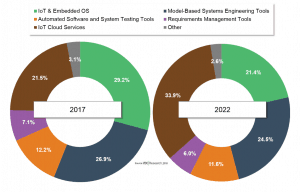
Source: VDC Research
From the Tier 1, Tier 2, silicon, and OS vendor perspective, the autonomous platform market is quite immature relative to the traditional revenue streams from body electronics, powertrain, and in-vehicle infotainment (IVI) markets.
The report details the five key sub-segments of the automotive software market where vendors currently derive substantial revenue: IoT & embedded operating systems (OSs), automated software & security testing (ASST), Model-based systems engineering tools (MBSE), requirements management tools (RM), and IoT cloud services.
These markets are more mature and are closely linked by strict coding standards and development processes (such as ISO26262) that enforce the quality and acceptable risk levels of the embedded software and the tools used to develop them.



